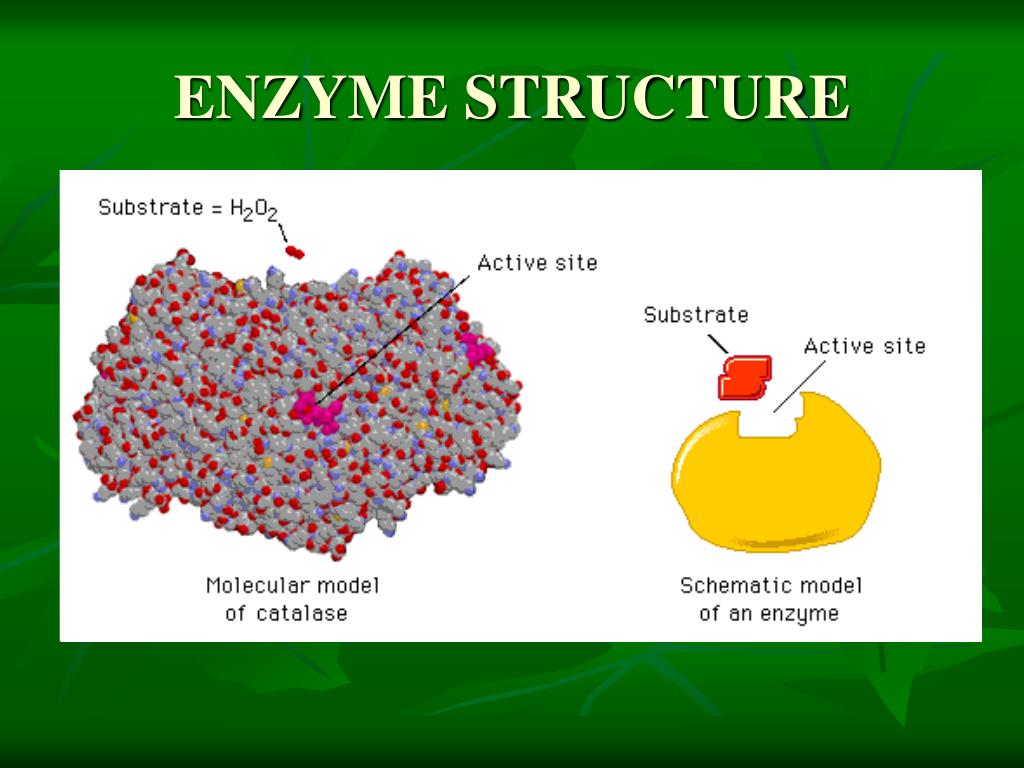
Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry . Explain how enzymes are classified and named. enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed. An enzyme is a protein biomolecule that acts as a biocatalyst by regulating the rate of various metabolic reactions. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. explain the functions of enzymes. what are enzymes? enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward.
from www.slideserve.com
enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. what are enzymes? explain the functions of enzymes. An enzyme is a protein biomolecule that acts as a biocatalyst by regulating the rate of various metabolic reactions. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed. Explain how enzymes are classified and named. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward.
PPT ENZYMES PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1117093
Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. Explain how enzymes are classified and named. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. An enzyme is a protein biomolecule that acts as a biocatalyst by regulating the rate of various metabolic reactions. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. what are enzymes? explain the functions of enzymes. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed. enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT ENZYMES CLASSIFICATION, STRUCTURE PowerPoint Presentation, free Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry what are enzymes? an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed. explain the functions of enzymes. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. Explain how enzymes are classified and named. The active site. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From studyflix.de
Enzyme • Definition, Aufbau und Funktion · [mit Video] Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. what are enzymes? Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. explain the functions of enzymes. enzymes are. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From www.thoughtco.com
Enzyme Biochemistry What They Are and How They Work Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry what are enzymes? enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. Explain how enzymes are classified and named. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. An enzyme is a protein biomolecule. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
Enzyme Definition and Classification YouTube Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. Most catalysts, but not all, are made. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1940469 Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. explain the functions of enzymes. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. An enzyme is a protein biomolecule that acts as a biocatalyst by regulating the rate of various metabolic reactions. an enzyme is. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From present5.com
Enzyme Structure classification and mechanism of action Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry An enzyme is a protein biomolecule that acts as a biocatalyst by regulating the rate of various metabolic reactions. enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. explain the functions of enzymes. Explain how enzymes are classified and named. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From exodmrxyv.blob.core.windows.net
Enzyme Activity Definition at Debra Holmes blog Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. An enzyme is a protein biomolecule that acts as a biocatalyst by regulating. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From www.slideshare.net
Enzymes Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. explain the functions. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From www.thoughtco.com
Structure and Function of an Enzyme Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. what are enzymes? explain. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
Enzyme and mechanism of enzymes, class 12th surface chemistry YouTube Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry Explain how enzymes are classified and named. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. An enzyme is a protein biomolecule that acts as a biocatalyst by regulating the rate of various metabolic reactions. enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Enzymes Activation Energy Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry Explain how enzymes are classified and named. explain the functions of enzymes. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. An enzyme is a protein biomolecule that acts as a biocatalyst by regulating the rate of various metabolic reactions. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
Specificity of Enzymes Biology Class 9 YouTube Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry explain the functions of enzymes. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed. what are enzymes? The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. An enzyme is a protein biomolecule. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From chemistrytalk.org
Enzymes Function and Types ChemTalk Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry what are enzymes? Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed. The active site is usually a small region (10% to 20%) within the. Explain how enzymes are classified and named.. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From ibiologia.com
Enzymes Definition, Classification & Functions Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry An enzyme is a protein biomolecule that acts as a biocatalyst by regulating the rate of various metabolic reactions. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed. . Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From www.aquaportail.com
Enzyme définition et explications Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. Explain how enzymes are classified and named. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. what are enzymes? enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary,. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
2. Enzyme Definition and classification YouTube Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed. enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and tertiary structures. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward.. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From www.biologynotes.in
Enzyme Specificity Definition, Types, Examples and Importance Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. An enzyme is a protein biomolecule that acts as a biocatalyst by regulating the rate of various metabolic reactions. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. enzymes are usually proteins having primary, secondary, and. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.
From ibiologia.com
Enzymes Definition, Classification & Functions Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry Explain how enzymes are classified and named. enzymes are highly specific and function in aqueous solutions under very mild conditions of temperature and ph. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. An enzyme is a protein biomolecule that acts as a biocatalyst by regulating the rate of various metabolic reactions. what. Enzyme Definition Physical Chemistry.